
Understanding Constant Bit Rate: A Comprehensive Guide
Constant Bit Rate (CBR) is a term that is widely used in the field of digital communication and multimedia. It refers to a transmission rate that remains constant throughout the duration of a data transfer. This article aims to provide you with a detailed and multi-dimensional introduction to CBR, covering its definition, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and real-world examples.
What is Constant Bit Rate?
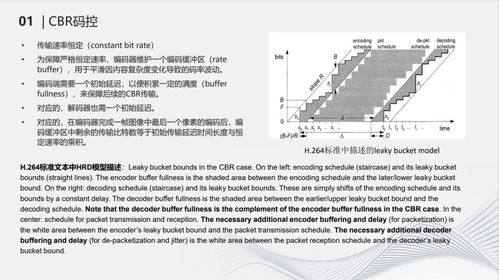
Constant Bit Rate is a method of transmitting data where the bit rate remains constant. This means that the amount of data transmitted per unit of time is consistent. In other words, the data is sent at a steady pace, without any fluctuations. This is in contrast to Variable Bit Rate (VBR), where the bit rate can vary depending on the complexity of the data.
How Does Constant Bit Rate Work?
CBR works by allocating a fixed amount of bandwidth for the data transmission. This fixed bandwidth is used to send the data at a constant rate. The sender and receiver both need to be synchronized to ensure that the data is transmitted and received at the correct rate. This synchronization is typically achieved through the use of timing signals and protocols.
Applications of Constant Bit Rate
CBR is used in various applications where a consistent and predictable data rate is required. Some of the most common applications include:
-
Telephony: CBR is used in traditional telephony to ensure that voice signals are transmitted at a constant rate, resulting in clear and uninterrupted communication.
-
Video Streaming: CBR is used in video streaming applications to maintain a consistent video quality, as the bit rate remains constant throughout the transmission.
-
Audio Streaming: Similar to video streaming, CBR is used in audio streaming to ensure a consistent audio quality.
-
VoIP: CBR is used in Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) to maintain a consistent voice quality during calls.
Advantages of Constant Bit Rate
There are several advantages to using CBR:
-
Consistency: CBR ensures that the data is transmitted at a consistent rate, which is beneficial for applications that require a predictable data flow.
-
Quality: CBR can help maintain a consistent quality of service, as the bit rate remains constant throughout the transmission.
-
Compatibility: CBR is compatible with a wide range of devices and systems, making it a versatile choice for various applications.
Disadvantages of Constant Bit Rate
Despite its advantages, CBR also has some disadvantages:
-
Inefficiency: CBR can be inefficient in terms of bandwidth usage, as it allocates a fixed amount of bandwidth even when the data does not require it.
-
Lack of Flexibility: CBR does not adapt to changes in data complexity, which can lead to underutilization of bandwidth during periods of low data complexity.
-
Quality Degradation: In some cases, CBR may not be able to maintain a consistent quality of service, especially when the network conditions are poor.
Real-World Examples of Constant Bit Rate
Here are some real-world examples of CBR in action:
| Application | Example |
|---|---|
| Telephony | Traditional landline phones use CBR to ensure clear and uninterrupted voice communication. |
| Video Streaming | YouTube uses CBR to maintain a consistent video quality for its users. |
| Audio Streaming | Spotify uses CBR to ensure a consistent audio quality for its users. |
| VoIP | Skype uses CBR to maintain a consistent voice quality during calls. |
In conclusion, Constant Bit Rate is a valuable tool in the field of digital communication and multimedia. Its ability to provide a consistent and predictable data rate makes it suitable for various applications. However, it is important to consider its limitations




