
Understanding Bit Rate: A Comprehensive Guide
Bit rate, often abbreviated as “bitrate,” is a term that you might have encountered while dealing with digital audio or video files. It refers to the amount of data that is processed or transmitted in a given unit of time. This article will delve into the intricacies of bit rate, its significance, and how it affects the quality of your digital media.
What is Bit Rate?
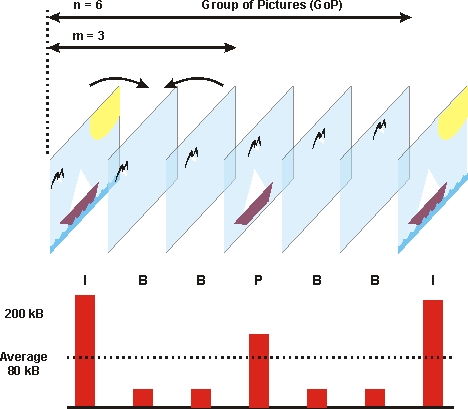
Bit rate is measured in bits per second (bps) and is a critical factor in determining the quality and size of your digital files. It represents the number of bits that are processed or transmitted in one second. For example, a file with a bit rate of 1 Mbps (megabits per second) processes or transmits 1 million bits every second.
Types of Bit Rate

There are several types of bit rates, each with its own characteristics and applications:
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Constant Bit Rate (CBR) | Stays constant throughout the file, regardless of the content’s complexity. | MP3 files often use CBR. |
| Variable Bit Rate (VBR) | Adapts to the content’s complexity, using more bits for complex scenes and fewer for simple ones. | High-quality video files often use VBR. |
| Average Bit Rate (ABR) | Represents the average bit rate of the file. | ABR is commonly used in streaming services. |
Bit Rate and File Size
The bit rate directly affects the file size of your digital media. A higher bit rate means a larger file size, as more data is being processed or transmitted. Conversely, a lower bit rate results in a smaller file size, but it may also lead to a decrease in quality. Here’s a simple formula to calculate the file size:
File Size (in bytes) = Bit Rate (in bits per second) 脳 Time (in seconds) / 8
Bit Rate and Quality
The quality of your digital media is closely related to its bit rate. A higher bit rate generally results in better quality, as more data is available to represent the audio or video content. However, this doesn’t always mean that a higher bit rate is better. The optimal bit rate depends on the specific content and your requirements.
Bit Rate in Different Formats
Bit rate varies across different digital media formats. Here are some common formats and their typical bit rates:
| Format | Typical Bit Rate |
|---|---|
| MP3 | 32 kbps to 320 kbps |
| FLAC | 16 kbps to 24 bits/44.1 kHz |
| MP4 | 500 kbps to 10 Mbps |
| AVI | 1 Mbps to 100 Mbps |
Bit Rate and Streaming
Bit rate is also crucial in streaming services. A higher bit rate ensures better quality, but it may also require more bandwidth. Streaming services often offer multiple bit rate options to cater to different user needs and network conditions.
Conclusion
Understanding bit rate is essential for anyone dealing with digital audio or video files. It affects the file size, quality, and streaming performance of your media. By choosing the right bit rate, you can achieve the optimal balance between quality and file size for your specific needs.







