
32 Bit vs 64 Bit: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to computer architecture, the debate between 32-bit and 64-bit systems has been ongoing for years. As a user, you might be wondering what the difference is and why it matters. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of both systems, comparing their performance, compatibility, and overall impact on your computing experience.
Understanding the Basics
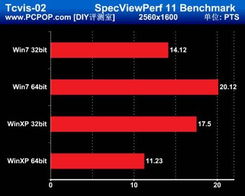
Before we dive into the specifics, let’s clarify what 32-bit and 64-bit systems actually mean. Both refer to the size of the data registers in the central processing unit (CPU). A 32-bit system can handle data in chunks of 32 bits, while a 64-bit system can handle data in chunks of 64 bits. This difference in size has significant implications for performance and compatibility.
Performance: The Heart of the Matter
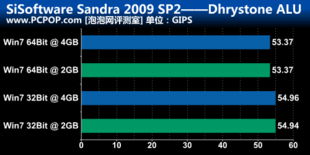
One of the most significant differences between 32-bit and 64-bit systems is their performance. Generally, 64-bit systems offer better performance due to their larger data registers. This allows them to process more data at once, resulting in faster execution times for applications and tasks. Here’s a breakdown of the key performance factors:
| Factor | 32-bit | 64-bit |
|---|---|---|
| Memory Addressing | Limited to 4GB of RAM | Supports up to 16TB of RAM |
| Processor Speed | Varies by CPU model | Generally faster due to larger data registers |
| Application Performance | Varies by application | Generally faster for memory-intensive tasks |
As you can see, 64-bit systems have a clear advantage in terms of memory addressing and processor speed. This makes them ideal for running resource-intensive applications, such as video editing software or 3D rendering programs.
Compatibility: Navigating the Landscape
While 64-bit systems offer superior performance, compatibility can be a concern. Many older applications and operating systems are still designed for 32-bit systems. Here’s a closer look at the compatibility issues you might encounter:
-
32-bit Applications: Many older applications are not compatible with 64-bit systems. This is because they rely on the limited memory addressing capabilities of 32-bit systems. To run these applications, you may need to install a 32-bit version of the operating system or use compatibility layers.
-
32-bit Drivers: Similar to applications, many drivers for hardware devices are designed for 32-bit systems. This can lead to issues when trying to install or update drivers on a 64-bit system.
-
Operating Systems: While most modern operating systems support both 32-bit and 64-bit versions, some older systems only offer 32-bit support.
It’s important to note that many newer applications and drivers are designed to be compatible with both 32-bit and 64-bit systems. This makes the transition from 32-bit to 64-bit systems smoother for most users.
Security: A Closer Look
In addition to performance and compatibility, security is another important factor to consider when comparing 32-bit and 64-bit systems. Here’s a breakdown of the key security aspects:
-
Memory Protection: 64-bit systems offer improved memory protection, making it more difficult for malicious software to exploit vulnerabilities in the system.
-
Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR): ASLR is a security feature that helps prevent buffer overflow attacks. 64-bit systems generally support ASLR better than 32-bit systems.
-
Hardware Support: 64-bit systems often have better hardware support for security features, such as AES encryption and secure boot.
While 64-bit systems offer improved security, it’s important to note that no system is completely immune to threats. Regularly updating your software and using strong passwords are essential for maintaining a secure computing environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the debate between 32-bit and 64-bit systems is a complex one.




