
32-bit or 64-bit: Understanding the Difference and Its Impact
When it comes to computer systems, the terms “32-bit” and “64-bit” are often thrown around, but what do they really mean? And how do they affect your computing experience? In this detailed exploration, we’ll delve into the nuances of these two architectures, their capabilities, and the implications they have on your daily computing tasks.
What is a Bit?
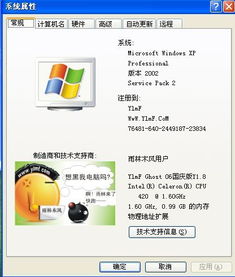
A bit is the smallest unit of data in a computer, representing either a 0 or a 1. The number of bits a computer can process at once is a crucial factor in determining its performance and capabilities.
32-bit Architecture
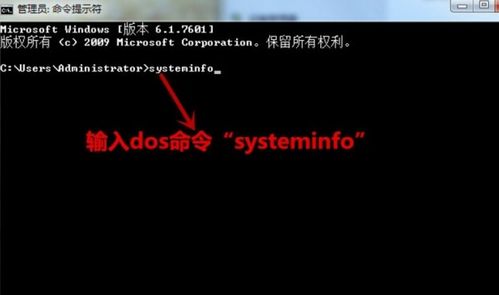
32-bit architecture has been around for quite some time and is still widely used in many devices. Here’s a closer look at its features:
-
Memory Addressing: A 32-bit architecture can address up to 4 GB of RAM. This means it can handle up to 4 GB of data at once, which was more than enough for most users in the early 2000s.
-
Processor Speed: 32-bit processors are generally slower than their 64-bit counterparts, as they can only process 32 bits of data at a time.
-
Compatibility: 32-bit operating systems can run on both 32-bit and 64-bit processors, but they can only utilize the full potential of 32-bit processors.
64-bit Architecture
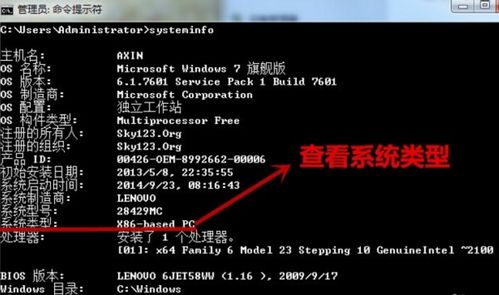
64-bit architecture has become the standard in modern computing. Here are some key points to consider:
-
Memory Addressing: A 64-bit architecture can address up to 18.4 million GB of RAM, which is significantly more than what a 32-bit architecture can handle. This allows for more efficient multitasking and better performance in memory-intensive applications.
-
Processor Speed: 64-bit processors are generally faster than 32-bit processors, as they can process 64 bits of data at a time, leading to improved performance in various tasks.
-
Compatibility: 64-bit operating systems can run on both 32-bit and 64-bit processors, but they can only utilize the full potential of 64-bit processors when running on a 64-bit system.
Impact on Performance
The performance difference between 32-bit and 64-bit architectures can be significant, especially in memory-intensive tasks. Here’s a comparison of some common scenarios:
| Task | 32-bit Performance | 64-bit Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Video Editing | Slower, limited to 4 GB of RAM | Faster, can utilize more than 4 GB of RAM |
| 3D Rendering | Slower, limited to 4 GB of RAM | Faster, can utilize more than 4 GB of RAM |
| Web Browsing | Little to no difference | Little to no difference |
Compatibility and Upgrades
When considering an upgrade from a 32-bit to a 64-bit system, it’s essential to ensure compatibility with your hardware and software. Here are some tips:
-
Hardware: Ensure your processor, motherboard, and RAM are compatible with a 64-bit operating system.
-
Software: Some older applications may not be compatible with 64-bit operating systems. Check for updates or alternative software that supports 64-bit architecture.
-
Operating System: Upgrade to a 64-bit operating system, such as Windows 10 or macOS Mojave, to take full advantage of your 64-bit hardware.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between 32-bit and 64-bit architectures is crucial for making informed decisions about your computing setup. While 32-bit systems may still be suitable for basic tasks, 64-bit systems offer superior performance, compatibility, and the ability to handle more memory-intensive applications. By considering the factors mentioned







