
64 Bit versus 32 Bit: A Comprehensive Comparison
When it comes to computer architecture, the debate between 64-bit and 32-bit systems has been ongoing for years. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of both systems, providing you with a detailed comparison from various dimensions. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or simply looking to understand the differences, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Processor Architecture
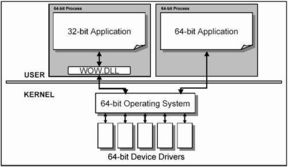
The primary difference between 64-bit and 32-bit processors lies in their ability to handle data. A 32-bit processor can process data in chunks of 32 bits, while a 64-bit processor can handle 64 bits at a time. This fundamental difference has a ripple effect on the overall performance and capabilities of the system.
| Feature | 32-bit Processor | 64-bit Processor |
|---|---|---|
| Data Handling | 32 bits at a time | 64 bits at a time |
| Memory Addressing | 4 GB of RAM | Up to 16 TB of RAM |
| Performance | Depends on the specific model | Generally faster for complex tasks |
Memory and Performance
One of the most significant advantages of a 64-bit processor is its ability to access more memory. While a 32-bit system is limited to 4 GB of RAM, a 64-bit system can handle up to 16 TB of RAM. This increased memory capacity allows for smoother multitasking and improved performance, especially when running memory-intensive applications.
Additionally, 64-bit processors are generally faster for complex tasks, such as video editing, 3D rendering, and scientific simulations. This is due to their ability to process larger chunks of data at once, reducing the time required for computations.
Compatibility and Software
While 64-bit systems offer numerous advantages, they may not be compatible with all software. Many older applications and operating systems are designed for 32-bit processors, which means they may not run correctly on a 64-bit system. However, most modern operating systems and applications are compatible with both architectures.
It’s essential to ensure that your software is compatible with the 64-bit architecture before making the switch. You can check the system requirements of your applications to determine their compatibility.
Energy Efficiency and Heat Dissipation
One area where 32-bit and 64-bit processors differ is energy efficiency and heat dissipation. Generally, 32-bit processors are more energy-efficient and generate less heat compared to their 64-bit counterparts. This is because 32-bit processors are designed to handle smaller data chunks, which requires less power and generates less heat.
However, the performance benefits of 64-bit processors often outweigh the energy efficiency concerns. In most cases, the increased performance justifies the higher energy consumption and heat generation.
Cost and Market Availability
When it comes to cost, 32-bit processors are generally more affordable than 64-bit processors. This is due to the lower manufacturing costs and wider availability of 32-bit components. However, the price difference may not be significant for high-end systems, where performance is a priority.
In terms of market availability, both 32-bit and 64-bit processors are widely available. However, 64-bit processors are becoming increasingly popular, especially in the consumer market, as more applications and operating systems support the architecture.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between 64-bit and 32-bit processors depends on your specific needs and requirements. While 64-bit processors offer numerous advantages, such as increased memory capacity and improved performance, they may not be compatible with all software and can be more expensive. Ultimately, it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons before making a decision.







