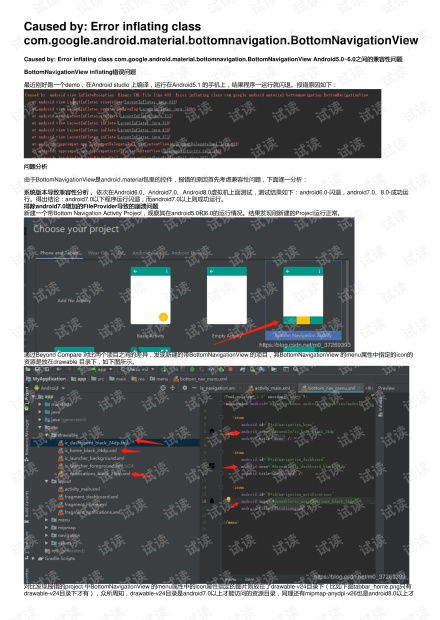
Understanding 256-bit Encryption Used by Banks
When it comes to securing your financial information, the use of 256-bit encryption by banks is a cornerstone of modern security practices. This article delves into the intricacies of this advanced encryption method, explaining how it works, its benefits, and its significance in the banking industry.
What is 256-bit Encryption?

256-bit encryption is a type of encryption that uses a 256-bit key to encrypt and decrypt data. This key is a sequence of 256 binary digits (bits), which can be either 0 or 1. The length of the key determines the strength of the encryption. A longer key means more possible combinations, making it more difficult for an attacker to crack the code.
How Does 256-bit Encryption Work?
256-bit encryption works by using a complex algorithm to transform plaintext (the original data) into ciphertext (encrypted data). This process is known as encryption. To decrypt the ciphertext back into plaintext, the same algorithm is used with the correct key. The strength of 256-bit encryption lies in the fact that it would take an enormous amount of computing power to crack the code, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized users to access your sensitive information.
Benefits of 256-bit Encryption in Banking

There are several benefits of using 256-bit encryption in the banking industry:
-
Security: The primary benefit is the enhanced security it provides. With 256-bit encryption, your financial information is much safer from cyber attacks and unauthorized access.
-
Confidentiality: 256-bit encryption ensures that your personal and financial data remains confidential, as it is almost impossible for anyone to intercept and decipher the information.
-
Compliance: Many regulatory bodies require financial institutions to use strong encryption methods to protect customer data. 256-bit encryption helps banks comply with these regulations.
-
Trust: By using 256-bit encryption, banks can build trust with their customers, knowing that their sensitive information is well-protected.
How 256-bit Encryption Protects Your Data
When you perform a transaction online, such as transferring funds or paying a bill, your data is encrypted using 256-bit encryption. This means that even if someone intercepts the data, they will not be able to read it without the correct key. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how it works:
-
You enter your personal and financial information into the bank’s website or mobile app.
-
The information is encrypted using a 256-bit key, turning it into ciphertext.
-
The encrypted data is sent over the internet to the bank’s server.
-
The bank’s server decrypts the ciphertext using the same 256-bit key, converting it back into plaintext.
This process ensures that your data remains secure throughout the transaction.
Comparing 256-bit Encryption with Other Encryption Methods
256-bit encryption is one of the strongest encryption methods available. Here’s a comparison with other common encryption methods:
| Encryption Method | Key Length | Security Level |
|---|---|---|
| 128-bit Encryption | 128 bits | Relatively secure, but can be broken with sufficient computing power |
| 256-bit Encryption | 256 bits | Extremely secure, nearly impossible to crack with current technology |
| 512-bit Encryption | 512 bits | Even more secure than 256-bit encryption, but less commonly used |
As you can see, 256-bit encryption is significantly more secure than 128-bit encryption, making it the preferred choice for protecting sensitive financial information.
Conclusion
256-bit encryption is a crucial component of modern banking security. By using this advanced encryption method, banks can ensure that your personal and financial information remains secure from cyber threats. As technology continues to evolve, it’s essential for banks to stay ahead of the curve and implement the strongest security measures possible. 256-bit encryption is




