
Quantum Bits: The Building Blocks of the Future
Quantum bits, often referred to as qubits, are the fundamental units of quantum computing. Unlike classical bits, which can be either 0 or 1, qubits can exist in a state of superposition, meaning they can be both 0 and 1 simultaneously. This unique property allows quantum computers to perform complex calculations at speeds that are unimaginable with classical computers. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of quantum bits, their significance, and the potential they hold for the future.
Understanding Quantum Bits
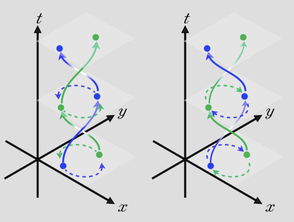 To grasp the concept of quantum bits, it’s essential to understand the principles of quantum mechanics. Quantum mechanics is a branch of physics that deals with the behavior of particles at the smallest scales, such as atoms and subatomic particles. One of the key principles of quantum mechanics is superposition, which allows particles to exist in multiple states simultaneously.In the context of quantum computing, superposition is what enables qubits to represent both 0 and 1 at the same time. This property is crucial for the exponential growth in computational power that quantum computers promise. To illustrate this, consider a classical bit as a coin that can land on either heads or tails. A qubit, on the other hand, is like a coin that can land on heads, tails, or both simultaneously.
To grasp the concept of quantum bits, it’s essential to understand the principles of quantum mechanics. Quantum mechanics is a branch of physics that deals with the behavior of particles at the smallest scales, such as atoms and subatomic particles. One of the key principles of quantum mechanics is superposition, which allows particles to exist in multiple states simultaneously.In the context of quantum computing, superposition is what enables qubits to represent both 0 and 1 at the same time. This property is crucial for the exponential growth in computational power that quantum computers promise. To illustrate this, consider a classical bit as a coin that can land on either heads or tails. A qubit, on the other hand, is like a coin that can land on heads, tails, or both simultaneously.
Quantum Superposition and Entanglement
 Quantum superposition is just one aspect of quantum computing. Another crucial concept is entanglement, which occurs when two or more qubits become correlated in such a way that the state of one qubit is dependent on the state of another, regardless of the distance between them. This phenomenon is known as quantum entanglement.Entanglement allows quantum computers to perform certain calculations much faster than classical computers. For example, a quantum computer using entangled qubits can solve certain types of problems in polynomial time, while a classical computer would require exponential time.
Quantum superposition is just one aspect of quantum computing. Another crucial concept is entanglement, which occurs when two or more qubits become correlated in such a way that the state of one qubit is dependent on the state of another, regardless of the distance between them. This phenomenon is known as quantum entanglement.Entanglement allows quantum computers to perform certain calculations much faster than classical computers. For example, a quantum computer using entangled qubits can solve certain types of problems in polynomial time, while a classical computer would require exponential time.
Quantum entanglement has been experimentally demonstrated in various ways, including the famous Bell’s inequality experiment. In this experiment, two entangled particles are separated by a large distance, and their properties are measured. The results show that the particles are correlated in a way that cannot be explained by classical physics, thus confirming the existence of quantum entanglement.
Quantum Bits in Practice
 While the theoretical understanding of quantum bits is well-established, practical implementation remains a significant challenge. One of the main challenges is maintaining the coherence of qubits, as they are highly sensitive to their environment and can easily lose their quantum state, a phenomenon known as decoherence.Several approaches have been developed to mitigate decoherence and create stable qubits. One of the most promising methods is the use of superconducting circuits, which involve using the quantum properties of electrons in a superconducting material to create qubits. Another approach is the use of trapped ions, where charged ions are confined in a vacuum and manipulated using electromagnetic fields.
While the theoretical understanding of quantum bits is well-established, practical implementation remains a significant challenge. One of the main challenges is maintaining the coherence of qubits, as they are highly sensitive to their environment and can easily lose their quantum state, a phenomenon known as decoherence.Several approaches have been developed to mitigate decoherence and create stable qubits. One of the most promising methods is the use of superconducting circuits, which involve using the quantum properties of electrons in a superconducting material to create qubits. Another approach is the use of trapped ions, where charged ions are confined in a vacuum and manipulated using electromagnetic fields.
Table 1: Comparison of Different Quantum Bit Technologies
| Technology | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Superconducting Circuits | High coherence times, scalable | Complex to fabricate, sensitive to noise |
| Trapped Ions | High coherence times, long coherence times | Expensive, limited scalability |
| Topological Qubits | Robust against noise, long coherence times | Difficult to implement, theoretical |
The Potential of Quantum Bits
The potential of quantum bits is immense, and they have the potential to revolutionize various fields, including cryptography, material science, and optimization problems. In cryptography, quantum computers can break certain types of encryption algorithms, such as RSA, which are currently considered secure. This has led to the development of quantum-resistant encryption algorithms that can protect data against future quantum attacks.In material science, quantum computers can simulate the properties of materials at the atomic level, leading to the discovery of new materials with unique properties. This has significant implications for the development of new drugs, batteries, and other technologies.
Quantum computing is also expected to have a significant impact on optimization problems, such as logistics, finance, and energy. By solving these problems much faster than classical computers, quantum computers can lead to more efficient and cost-effective solutions.
Conclusion
Related Posts
mosquito bite up close,Mosquito Bite Up Close: A Detailed Look
Mosquito Bite Up Close: A Deta…
mosquito bites natural remedies,Understanding the Pesky Problem: Mosquito Bites
Understanding the Pesky Proble…




