
32 Bit Computer: A Comprehensive Guide for Understanding Its Capabilities and Limitations
Are you curious about the inner workings of a 32-bit computer? Do you want to understand its capabilities and limitations? Look no further! In this detailed guide, we will delve into the world of 32-bit computing, exploring its history, architecture, performance, and applications. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of what a 32-bit computer is and how it compares to its counterparts.
What is a 32-bit Computer?
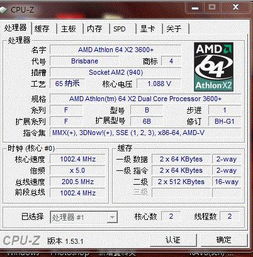
A 32-bit computer is a type of computer that uses a 32-bit processor architecture. This architecture allows the computer to process data in 32-bit chunks, which means it can handle a maximum of 4,294,967,296 unique values. This is significantly larger than the 8-bit architecture used in early computers, which could only handle 256 unique values.
History of 32-bit Computing
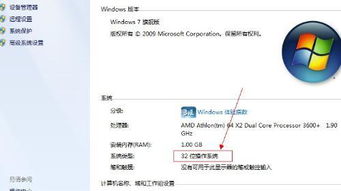
The concept of 32-bit computing dates back to the 1970s when Intel introduced the 8086 microprocessor. This processor was a significant leap forward in terms of performance and capability compared to its predecessors. Since then, 32-bit processors have become the standard in the computer industry, with various iterations and improvements over the years.
32-bit Architecture
The 32-bit architecture is based on the use of 32-bit registers, which are small storage locations within the processor that hold data. These registers are used to perform arithmetic and logical operations on data. A 32-bit processor can handle 32 bits of data at a time, which allows for faster processing and more efficient memory management.
One of the key features of the 32-bit architecture is the ability to address a large amount of memory. A 32-bit processor can address up to 4 GB of RAM, which is more than enough for most applications. However, due to limitations in the operating system, the actual amount of usable memory may be less.
Performance of 32-bit Computers
Compared to 64-bit computers, 32-bit computers may have some limitations in terms of performance. This is because 64-bit processors can handle larger amounts of data and have more registers, which can lead to faster processing. However, for many applications, the performance difference between 32-bit and 64-bit computers is negligible.
One of the main advantages of 32-bit computers is their lower cost and power consumption. This makes them a popular choice for budget-conscious consumers and mobile devices. Additionally, 32-bit operating systems are generally more lightweight and easier to use, which can be beneficial for older hardware.
Applications of 32-bit Computers
32-bit computers are used in a wide range of applications, from personal computers to embedded systems. Some common uses include:
- Personal Computers: Many older computers and laptops still use 32-bit operating systems, such as Windows XP and Windows 7.
- Mobile Devices: Many smartphones and tablets use 32-bit processors, as they are more power-efficient and cost-effective.
- Embedded Systems: 32-bit processors are commonly used in embedded systems, such as medical devices, industrial control systems, and consumer electronics.
Limitations of 32-bit Computers
While 32-bit computers have many advantages, they also have some limitations:
- Memory Limitations: As mentioned earlier, a 32-bit processor can address up to 4 GB of RAM. This can be a limitation for applications that require more memory.
- Performance Limitations: 32-bit processors may have slower performance compared to 64-bit processors, especially for tasks that require a lot of memory.
- Incompatibility: Some newer software and hardware may not be compatible with 32-bit operating systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a 32-bit computer is a type of computer that uses a 32-bit processor architecture. While it has some limitations, it remains a popular choice for many applications due to its lower cost and power consumption. By understanding the capabilities and limitations of 32-bit computing, you can make informed decisions about your computing needs.





