
Understanding Bits Per Second: A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever wondered what “bits per second” (bps) really means? It’s a term that’s often thrown around in discussions about internet speeds, data transfer, and network performance. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of bits per second, exploring its definition, significance, and how it affects your daily digital life.
What is Bits Per Second?
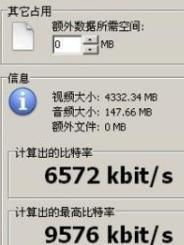
Bits per second is a unit of measurement used to describe the rate at which data is transferred. It’s a fundamental concept in digital communication, as it determines how quickly information can be sent and received. To put it simply, bps is the speed at which bits鈥攂inary digits, the smallest unit of information in computing鈥攖ravel through a network or a device.
For example, if you’re downloading a file from the internet, the download speed is measured in bits per second. The higher the bps value, the faster the file will be transferred to your device.
Understanding the Basics

Before we dive deeper into the world of bits per second, it’s essential to understand some basic concepts:
- Bit: A bit is the smallest unit of information in computing, represented by either a 0 or a 1.
- Byte: A byte is a group of 8 bits and is the standard unit of digital information storage.
- Bit Rate: The bit rate is the number of bits that can be transmitted or received in a given time frame, typically measured in bits per second (bps), kilobits per second (Kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), or gigabits per second (Gbps).
Common Bit Rate Units
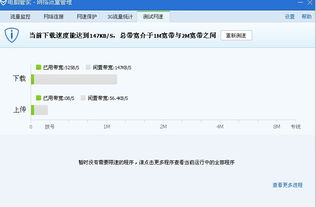
Now that we have a basic understanding of bits and bit rates, let’s explore the different units used to measure them:
| Unit | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| bps | Bits per second | 1,000 bps = 1 Kbps |
| Kbps | Kilobits per second | 1,000 Kbps = 1 Mbps |
| Mbps | Megabits per second | 1,000 Mbps = 1 Gbps |
| Gbps | Gigabits per second | 1,000 Gbps = 1 Tbps |
As you can see, each unit is 1,000 times larger than the previous one. This means that a 1 Gbps connection is 1,000 times faster than a 1 Mbps connection.
Factors Affecting Bit Rates
Several factors can affect the bit rate of a network or device:
- Network Infrastructure: The quality and capacity of the network infrastructure, such as cables, routers, and switches, can impact the bit rate.
- Distance: The distance between the sender and receiver can affect the bit rate, as signals may degrade over long distances.
- Interference: External factors, such as electromagnetic interference, can disrupt the signal and reduce the bit rate.
- Bandwidth: The available bandwidth of a network determines how much data can be transmitted at any given time.
Bit Rates in Different Applications
Bit rates vary depending on the application or use case:
- Web Browsing: A typical web browsing session requires a bit rate of around 1-5 Mbps.
- Email: Email communication typically requires a bit rate of around 1-2 Kbps.
- Streaming Video: High-definition streaming requires a bit rate of around 5-10 Mbps, while 4K streaming can require up to 25 Mbps or more.
- Online Gaming: Online gaming requires a bit





