
Early Stage Tick Bite: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the early stages of a tick bite is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Ticks are small arachnids that can transmit diseases to humans and animals. This guide will delve into the various aspects of an early stage tick bite, including symptoms, prevention, and treatment options.
Identifying a Tick Bite
Recognizing a tick bite is the first step in managing the situation. Ticks are typically small, often no larger than a pinhead, and can be difficult to spot. Here are some signs to look out for:
-
Redness or swelling around the bite area
-
A small, red bump that may resemble a mosquito bite
-
A small, dark spot on the skin where the tick was attached
It’s important to note that not all tick bites will result in disease transmission. However, if you suspect you’ve been bitten by a tick, it’s best to err on the side of caution and seek medical attention.
Understanding Tick-Borne Diseases
Tick bites can lead to various diseases, depending on the type of tick and the region you are in. Some of the most common tick-borne diseases include:
| Disease | Causing Tick | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Lyme Disease | Borrelia burgdorferi | Joint pain, fatigue, fever, headache, and a characteristic rash known as erythema migrans |
| Ehrlichiosis | Babesia microti | Fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, and fatigue |
| Anaplasmosis | Anaplasma phagocytophilum | Fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, and fatigue |
| Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever | Rickettsia rickettsii | Fever, headache, muscle aches, and a rash |
These diseases can be serious and may require long-term treatment. It’s essential to seek medical attention if you suspect you’ve been exposed to a tick-borne disease.
Preventing Tick Bites
Preventing tick bites is the best way to avoid tick-borne diseases. Here are some tips to help you stay safe:
-
Wear long sleeves and pants when hiking or working in tick-infested areas
-
Use insect repellents containing DEET or picaridin
-
Perform regular tick checks on yourself, your family, and your pets
-
Remove ticks promptly and carefully
By taking these precautions, you can significantly reduce your risk of tick bites and the diseases they may carry.
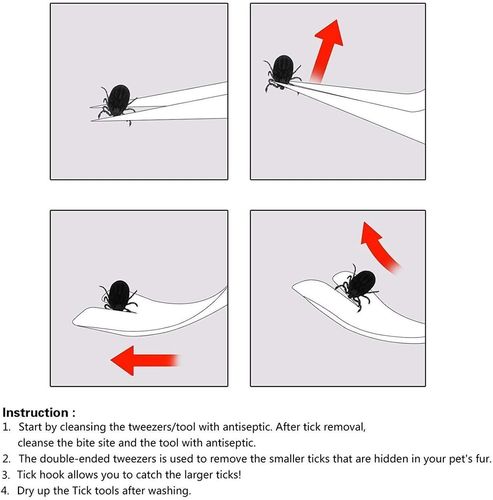
Removing a Tick
Removing a tick as soon as possible is crucial to prevent disease transmission. Here’s how to do it safely:
-
Grasp the tick’s head with a pair of fine-tipped tweezers as close to the skin as possible
-
Pull the tick straight up and away from the skin in one, smooth motion
-
Do not twist or pull the tick off the skin, as this may cause the mouthparts to break off and remain in the skin
-
Disinfect the bite area and your hands with alcohol or soap and water
After removing the tick, place it in a sealed container or crush it with a pair of clean tweezers. This will help you monitor for any signs of disease transmission.
Seeking Medical Attention
If you experience any symptoms of a tick-borne disease after a tick bite, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics or other treatments to prevent the disease







