
32 vs 64 Bit Windows: A Comprehensive Guide for Users
When it comes to choosing between a 32-bit and 64-bit version of Windows, it’s essential to understand the differences and how they can impact your computing experience. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of both versions, comparing their capabilities, system requirements, and performance. Let’s explore the world of 32-bit and 64-bit Windows together.
Understanding the Basics

Before we dive into the details, let’s clarify what 32-bit and 64-bit mean. These terms refer to the size of the data registers used by the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer. A 32-bit system can handle data in chunks of 32 bits, while a 64-bit system can handle data in chunks of 64 bits. This difference in data handling capacity has significant implications for system performance and compatibility.
System Requirements
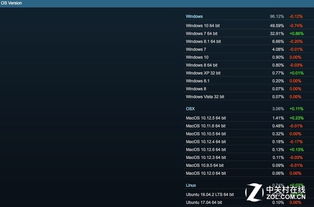
One of the first things to consider when choosing between 32-bit and 64-bit Windows is your system’s hardware. A 64-bit system requires a 64-bit CPU, which is more powerful and capable of handling larger amounts of data. If your computer has a 32-bit CPU, you’ll be limited to using the 32-bit version of Windows, regardless of whether you install it on a 64-bit machine.
Here’s a table summarizing the minimum system requirements for both versions of Windows:
| Component | 32-bit Windows | 64-bit Windows |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | 32-bit CPU | 64-bit CPU |
| Memory | 1 GB RAM | 2 GB RAM |
| Graphics Card | DirectX 9 graphics with WDDM driver | DirectX 9 graphics with WDDM driver |
| Storage | 16 GB available disk space | 20 GB available disk space |
Performance and Compatibility
One of the primary advantages of a 64-bit system is its ability to handle more memory. This can lead to improved performance, especially when running memory-intensive applications such as video editing software or virtual machines. Additionally, 64-bit systems can take advantage of larger amounts of RAM, which can further enhance performance.
However, it’s important to note that not all applications are compatible with 64-bit Windows. Some older or less common applications may only be available in 32-bit versions. In such cases, you may need to run these applications in a compatibility mode or use a virtual machine to run the 32-bit version of Windows.
Security and Stability
64-bit Windows generally offers improved security and stability compared to its 32-bit counterpart. This is due to the larger address space, which makes it more difficult for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities. Additionally, 64-bit systems often benefit from more advanced security features, such as address space layout randomization (ASLR) and data execution prevention (DEP).
Upgrading and Installation
Upgrading from a 32-bit to a 64-bit version of Windows can be a complex process. It’s important to ensure that your hardware and software are compatible with the new version. In some cases, you may need to perform a clean installation, which involves backing up your data and starting from scratch.
When installing a 64-bit version of Windows, you’ll need to choose between the “Custom” and “Express” installation options. The “Custom” option allows you to select individual partitions and customize the installation process, while the “Express” option automatically installs Windows on the recommended settings.
Conclusion
Choosing between a 32-bit and 64-bit version of Windows depends on your specific needs and hardware capabilities. A 64-bit system offers improved performance, compatibility, and security, but it may require more powerful hardware and compatibility with 64-bit applications. By understanding the differences between these two versions, you can make an informed decision that best suits your computing needs.







