
Insect Bite Hives: A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever experienced a sudden, itchy, and sometimes painful outbreak of red, raised bumps on your skin after being bitten by an insect? If so, you might be dealing with insect bite hives, also known as urticaria. This common skin condition can be caused by various factors, and it’s essential to understand its symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention to manage it effectively. Let’s delve into the details of insect bite hives to help you better understand this condition.
Understanding Insect Bite Hives
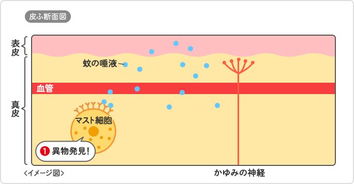
Insect bite hives are a type of urticaria, which is an allergic reaction to an insect bite. When your body encounters an allergen from an insect bite, it releases histamine and other chemicals, leading to the characteristic hive-like rash. These hives can appear anywhere on your body and may vary in size, shape, and duration.
Common Symptoms

The most common symptoms of insect bite hives include:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Hives | Red, raised bumps on the skin that may be itchy, painful, or burning |
| Swelling | Localized swelling around the hive area |
| Itching | Intense itching, which may worsen at night |
| Pain or burning sensation | Some individuals may experience pain or burning around the hive area |
| Wheezing or difficulty breathing | In severe cases, insect bite hives can trigger anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction |
Causes of Insect Bite Hives

Insect bite hives can be caused by various insects, including:
- Bees and wasps
- Ants
- Spiders
- Ticks
- Mosquitoes
- Flies
Some common causes of insect bite hives include:
- Direct contact with the insect’s venom
- Reaction to the insect’s saliva or other body fluids
- Genetic predisposition
- Environmental factors, such as pollen or mold
Treatment Options
Managing insect bite hives involves both immediate relief and long-term prevention. Here are some treatment options:
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec), can help alleviate itching and reduce swelling.
- Topical corticosteroids: Creams or ointments containing hydrocortisone can be applied to the affected area to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Oral corticosteroids: In severe cases, your doctor may prescribe oral corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.
- Immunosuppressants: In some cases, immunosuppressants may be prescribed to manage chronic or severe insect bite hives.
Prevention Tips
Preventing insect bite hives involves avoiding exposure to allergens and taking precautions to minimize the risk of insect bites. Here are some tips:
- Wear protective clothing, such as long sleeves and pants, when spending time in areas with high insect activity.
- Use insect repellents containing DEET or picaridin to deter insects.
- Keep your home and yard free of standing water, which can attract mosquitoes.
- Inspect your clothing and skin for ticks after spending time in wooded or grassy areas.
- Be aware of the types of insects that are prevalent in your area and take appropriate precautions.
Insect bite hives can be a frustrating and uncomfortable condition, but with proper management and prevention, you can minimize its impact on your daily





