Step Down Bit: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the concept of a step down bit is crucial for anyone involved in electronics, particularly in the field of power supply design. A step down bit, also known as a voltage regulator, is a device that reduces the voltage from a higher level to a lower level. This article will delve into the various aspects of step down bits, including their types, applications, and how they work.
Types of Step Down Bits

There are several types of step down bits available in the market, each with its own set of features and applications. The most common types include linear regulators, switching regulators, and LDO regulators.
| Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Regulators | These regulators use a series-pass element to dissipate excess voltage as heat. | Low-power applications, such as microcontrollers and sensors. |
| Switching Regulators | These regulators switch the input voltage on and off at a high frequency to control the output voltage. | High-power applications, such as power supplies for laptops and smartphones. |
| LDO Regulators | LDO stands for Low-Dropout, which means these regulators can maintain a stable output voltage even when the input voltage is close to the output voltage. | Applications requiring high precision, such as analog circuits and microcontrollers. |
How Step Down Bits Work
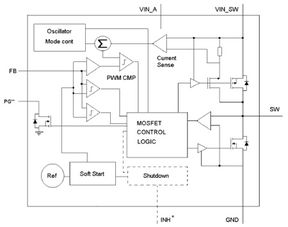
Step down bits work by converting the input voltage to a high-frequency AC signal, then rectifying and filtering the signal to obtain a stable DC output voltage. The process can be broken down into the following steps:
-
Input Voltage: The step down bit receives an input voltage, which can be from a battery, a power supply, or another voltage source.
-
Switching: The input voltage is switched on and off at a high frequency by a switching element, such as a transistor or a MOSFET.
-
Rectification: The high-frequency AC signal is rectified to a pulsating DC signal using a diode.
-
Filtering: The pulsating DC signal is filtered using an inductor and a capacitor to obtain a smooth and stable DC output voltage.
-
Control Loop: The output voltage is compared to a reference voltage, and the switching element is controlled accordingly to maintain the desired output voltage.
Applications of Step Down Bits
Step down bits are widely used in various applications, including:
-
Consumer Electronics: Step down bits are used in smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices to convert the high-voltage battery input to a lower voltage for the internal circuitry.
-
Power Supplies: Step down bits are used in power supplies to provide a stable and regulated output voltage for various electronic devices.
-
Automotive: Step down bits are used in automotive applications to convert the high-voltage battery input to a lower voltage for the internal electronic systems.
-
Industrial: Step down bits are used in industrial applications to provide a stable and regulated power supply for various equipment and machinery.
Choosing the Right Step Down Bit
Selecting the right step down bit for your application depends on several factors, including input voltage, output voltage, output current, and efficiency. Here are some tips to help you choose the right step down bit:
-
Input Voltage: Ensure that the input voltage of the step down bit is compatible with your power source.
-
Output Voltage: Choose a step down bit with an output voltage that meets your application requirements.
-
Output Current: Select a step down bit with an output current rating that can handle the load of your application.
-
Efficiency: Consider the efficiency of the step down bit, as it will affect the overall power consumption of your application.
-
Size and Cost: Choose





