
Bits in MAC Address: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the intricacies of a MAC address is crucial in today’s digital landscape. MAC addresses, or Media Access Control addresses, are unique identifiers assigned to network interfaces for communications on the physical network segment. This guide will delve into the various aspects of bits in a MAC address, providing you with a detailed insight into how they work and their significance.
What is a MAC Address?
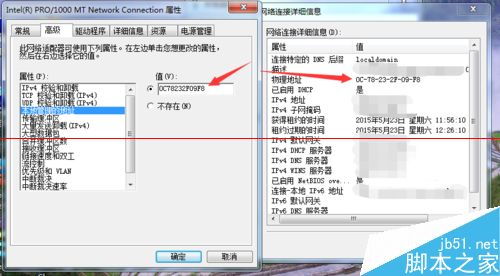
A MAC address is a 48-bit number that uniquely identifies a network interface controller (NIC) for communication on a network. It is typically represented as six groups of two hexadecimal digits, separated by colons or hyphens, such as 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E.
Structure of a MAC Address
The 48-bit MAC address is divided into two main parts: the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) and the Extender ID.
| Part | Bits | Description |
|---|---|---|
| OUI | 24 bits | Identifies the manufacturer of the network interface card. |
| Extender ID | 24 bits | Unique identifier for the network interface card within the manufacturer’s range. |
The OUI is assigned by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) to ensure that each manufacturer has a unique identifier. The Extender ID is assigned by the manufacturer and is used to differentiate their products.
How MAC Addresses are Generated
MAC addresses can be generated in two ways: manufacturer-assigned and randomly-generated.
Manufacturer-Assigned MAC Addresses:
Most MAC addresses are manufacturer-assigned. The manufacturer uses the OUI provided by the IEEE and assigns a unique Extender ID to each network interface card. This process ensures that each MAC address is unique and can be traced back to the manufacturer.
Randomly-Generated MAC Addresses:
In some cases, manufacturers may choose to generate MAC addresses randomly. This approach is often used in virtual environments or when a network interface card needs to be reassigned to a different device. Randomly-generated MAC addresses help prevent potential conflicts and ensure that each device has a unique identifier.
Importance of MAC Addresses
MAC addresses play a vital role in network communication. Here are some key reasons why they are important:
-
Unique Identification: MAC addresses ensure that each device on a network can be uniquely identified, allowing for efficient communication and data transfer.
-
Network Security: MAC addresses are used in various network security protocols, such as MAC address filtering, to control access to a network.
-
Network Management: MAC addresses help network administrators monitor and manage network traffic, identify devices, and troubleshoot issues.
Limitations of MAC Addresses
While MAC addresses are essential for network communication, they also have some limitations:
-
Static Nature: MAC addresses are typically static, meaning they do not change unless manually modified. This can make it challenging to manage devices in dynamic network environments.
-
Scalability: As the number of devices on a network grows, managing MAC addresses can become increasingly difficult.
-
Security Vulnerabilities: MAC addresses can be spoofed or cloned, potentially leading to security breaches.
Conclusion
Understanding the bits in a MAC address is crucial for anyone involved in network administration or security. By familiarizing yourself with the structure, generation, and importance of MAC addresses, you can better manage and secure your network. Remember that while MAC addresses are a valuable tool, they are not infallible and should be used in conjunction with other security measures.







