
Understanding the Difference: Audio 24 Bit vs 16 Bit
When it comes to audio quality, the bit depth plays a crucial role in determining the fidelity and clarity of the sound. In this article, we will delve into the nuances of 24-bit and 16-bit audio formats, comparing their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of which format suits your needs best.
What is Bit Depth?
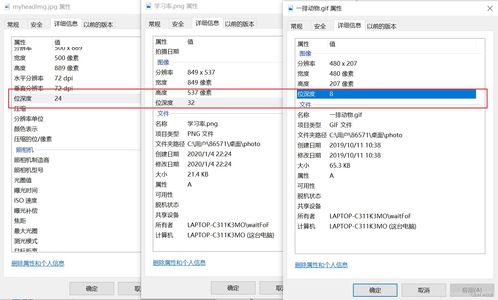
Bit depth refers to the number of bits used to represent the audio signal. It determines the dynamic range of the audio, which is the difference between the quietest and the loudest sounds that can be captured. A higher bit depth allows for a wider dynamic range, resulting in more accurate and detailed audio reproduction.
24-bit Audio: The Higher Resolution

24-bit audio uses 24 bits to represent each sample of the audio signal. This format offers a significantly wider dynamic range compared to 16-bit audio. Here’s a breakdown of the key features:
| Feature | 24-bit Audio | 16-bit Audio |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Range | 144 dB | 96 dB |
| Sample Rate | Up to 192 kHz | Up to 96 kHz |
| Bit Depth | 24 bits | 16 bits |
As you can see from the table, 24-bit audio offers a much wider dynamic range and higher sample rates. This results in more accurate and detailed audio reproduction, especially in complex and dynamic music genres.
Advantages of 24-bit Audio

1. Enhanced Dynamic Range: The wider dynamic range of 24-bit audio allows for more subtle and nuanced details in the audio signal, resulting in a more realistic and immersive listening experience.
2. Improved Clarity: With a higher bit depth, 24-bit audio can capture and reproduce more subtle nuances in the audio signal, leading to clearer and more defined sound.
3. Better Compatibility: Many modern audio devices and software support 24-bit audio, making it easier to work with and enjoy high-quality audio files.
Disadvantages of 24-bit Audio
1. Larger File Size: 24-bit audio files are larger in size compared to 16-bit files, which can be a concern for storage and streaming purposes.
2. Limited Compatibility: Some older audio devices and software may not support 24-bit audio, limiting its usability in certain scenarios.
16-bit Audio: The Standard Format
16-bit audio has been the standard format for many years, primarily due to its balance between quality and file size. Here’s a brief overview of its features:
1. Dynamic Range: 16-bit audio offers a dynamic range of 96 dB, which is sufficient for most consumer applications.
2. Sample Rate: The sample rate for 16-bit audio is typically up to 48 kHz, which is considered high-quality for most consumer purposes.
Advantages of 16-bit Audio
1. Smaller File Size: 16-bit audio files are smaller in size compared to 24-bit files, making them more suitable for storage and streaming.
2. Widespread Compatibility: 16-bit audio is widely supported by audio devices and software, ensuring seamless compatibility across various platforms.
Disadvantages of 16-bit Audio
1. Limited Dynamic Range: The narrower dynamic range of 16-bit audio can result in a less detailed and less immersive listening experience, especially in complex and dynamic music genres.
2. Potential for Clipping: Due to the limited dynamic range, 16-bit audio is more prone to clipping, which can distort the sound quality.
Conclusion
Choosing between 24-bit and 16-bit audio depends on your specific needs and preferences. If you’re looking for the highest quality and are not concerned about file size or compatibility issues, 24-bit audio is the way to go. However, if you need a balance between quality and file size, or if compatibility is a priority, 16-bit audio is a






